Most Recent Juniper JN0-480 Exam Questions & Answers
Prepare for the Juniper Data Center, Specialist exam with our extensive collection of questions and answers. These practice Q&A are updated according to the latest syllabus, providing you with the tools needed to review and test your knowledge.
QA4Exam focus on the latest syllabus and exam objectives, our practice Q&A are designed to help you identify key topics and solidify your understanding. By focusing on the core curriculum, These Questions & Answers helps you cover all the essential topics, ensuring you're well-prepared for every section of the exam. Each question comes with a detailed explanation, offering valuable insights and helping you to learn from your mistakes. Whether you're looking to assess your progress or dive deeper into complex topics, our updated Q&A will provide the support you need to confidently approach the Juniper JN0-480 exam and achieve success.
The questions for JN0-480 were last updated on Jan 21, 2025.
- Viewing page 1 out of 13 pages.
- Viewing questions 1-5 out of 65 questions
Which two statements are correct regarding a pristine configuration in Juniper Apstra? (Choose two.)
The following two statements are incorrect in this scenario:
Exhibit.

In the EVPN-VXLAN data center fabric bridged overlay architecture shown in the exhibit, the servers are connected to Lead and Leat6 using the same virtual network identifier (VNI).
Which two statements are correct in this scenario? (Choose two.)
In the EVPN-VXLAN data center fabric bridged overlay architecture shown in the exhibit, the servers are connected to Leaf1 and Leaf6 using the same virtual network identifier (VNI). This means that the servers belong to the same Layer 2 domain and can communicate with each other using VXLAN tunnels across the fabric. The underlay network provides the IP connectivity between the leaf and spine devices, and it uses EBGP as the routing protocol. Therefore, the following two statements are correct in this scenario:
Loopback IPv4 addresses must be advertised into the EBGP underlay from leaf and spine devices. This is because the loopback addresses are used as the source and destination IP addresses for the VXLAN tunnels, and they must be reachable by all the devices in the fabric. The loopback addresses are also used as the router IDs and the BGP peer addresses for the EBGP sessions.
The underlay EBGP peering's must be established between leaf and spine devices. This is because the EBGP sessions are used to exchange the underlay routing information and the EVPN routes for the overlay network. The EBGP sessions are established using the loopback addresses of the devices, and they follow a spine-and-leaf topology, where each leaf device peers with all the spine devices, and each spine device peers with all the leaf devices.
The following two statements are incorrect in this scenario:
The underlay must use IRB interfaces. This is not true, because the underlay network does not provide any Layer 3 gateway functionality for the overlay network. The IRB interfaces are used to provide inter-VXLAN routing within the fabric, which is not the case in the bridged overlay architecture. The IRB interfaces are used in the edge-routed bridging (ERB) or the centrally-routed bridging (CRB) architectures, which are different from the bridged overlay architecture.
The underlay must be provisioned with PIMv2. This is not true, because the underlay network does not use multicast for the VXLAN tunnels. The VXLAN tunnels are established using EVPN, which uses BGP to distribute the MAC and IP addresses of the end hosts and the VTEP information of the devices. EVPN eliminates the need for multicast in the underlay network, and it provides optimal forwarding and fast convergence for the overlay network.
Exploring EVPN-VXLAN Overlay Architectures -- Bridged Overlay
Exhibit.
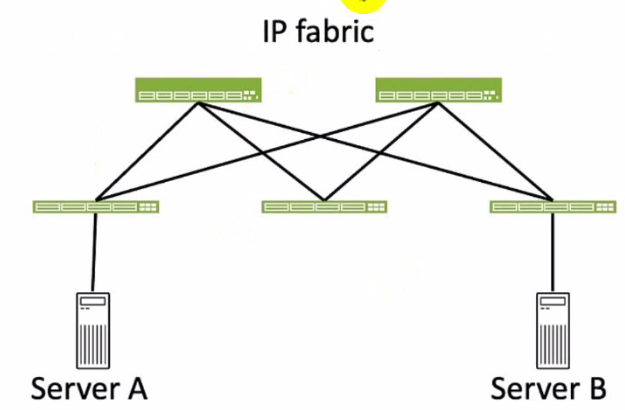
Referring to the exhibit, how many broadcast domains will an Ethernet frame pass through when traversing the IP fabric from Server A to Server B?
In the exhibit, there are two broadcast domains that an Ethernet frame will pass through when traversing the IP fabric from Server A to Server B. The first broadcast domain is the one that contains Server A and the leaf device that it is connected to. The second broadcast domain is the one that contains Server B and the leaf device that it is connected to. The IP fabric itself is not a broadcast domain, because it uses IP routing and VXLAN encapsulation to transport the Ethernet frames over the Layer 3 network. Therefore, the statement C is correct in this scenario.
The following three statements are incorrect in this scenario:
A) 1. This is not true, because there are not one, but two broadcast domains that an Ethernet frame will pass through when traversing the IP fabric from Server A to Server B. The IP fabric itself is not a broadcast domain, because it uses IP routing and VXLAN encapsulation to transport the Ethernet frames over the Layer 3 network.
B) 4. This is not true, because there are not four, but two broadcast domains that an Ethernet frame will pass through when traversing the IP fabric from Server A to Server B. The spine devices and the leaf devices that are not connected to the servers are not part of the broadcast domains, because they use IP routing and VXLAN encapsulation to transport the Ethernet frames over the Layer 3 network.
D) 3. This is not true, because there are not three, but two broadcast domains that an Ethernet frame will pass through when traversing the IP fabric from Server A to Server B. The IP fabric itself is not a broadcast domain, because it uses IP routing and VXLAN encapsulation to transport the Ethernet frames over the Layer 3 network.
You are using Juniper Apstra to design a data center fabric.
In this scenario, which object type associates a specific vendor model to a logical device?
Unlock All Questions for Juniper JN0-480 Exam
Full Exam Access, Actual Exam Questions, Validated Answers, Anytime Anywhere, No Download Limits, No Practice Limits
Get All 65 Questions & Answers